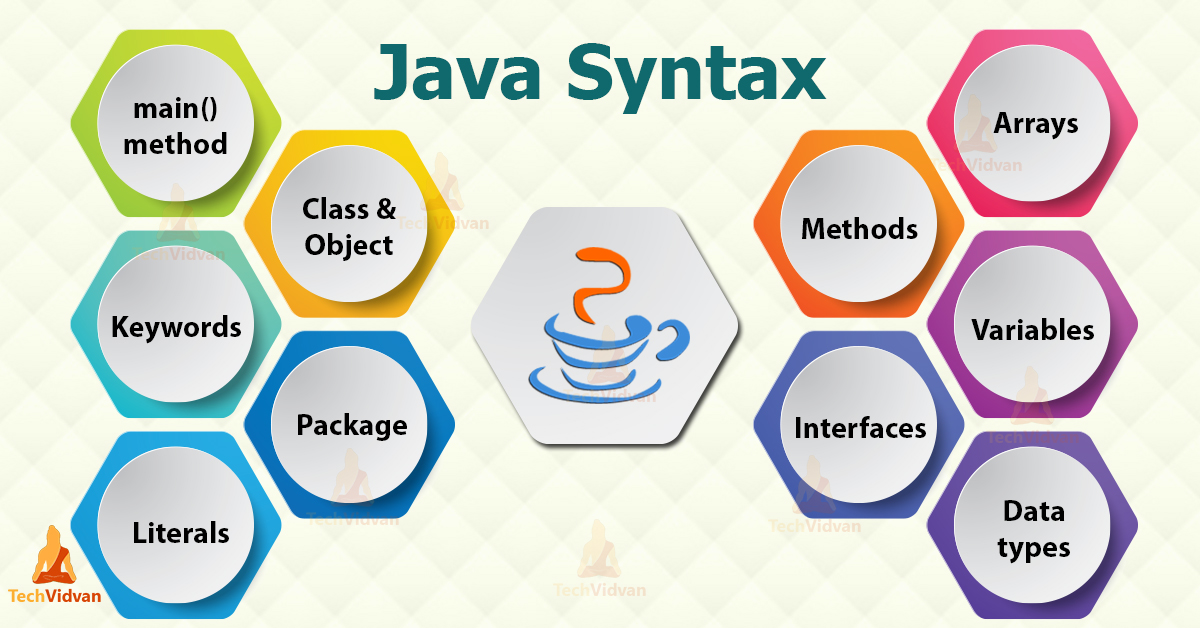
Java is a high-leel, object-oriented programming language renowned for its portability, reliability, and versatility. Developed by Sun Microsystems (now owned by Oracle Corporation) in the mid-1990s, Java has since become one of the most widely used programming languages globally. Its popularity stems from its ability to run on any platform with a Java Virtual Machine (JVM), enabling developers to write code once and deploy it across various operating systems and devices.
At its core, Java is designed to be simple, robust, and secure. It follows the principle of "write once, run anywhere," achieved through its compilation process. Java source code is compiled into an intermediate representation called bytecode, which is then executed by the JVM. This abstraction shields developers from platform-specific details, making Java programs highly portable.
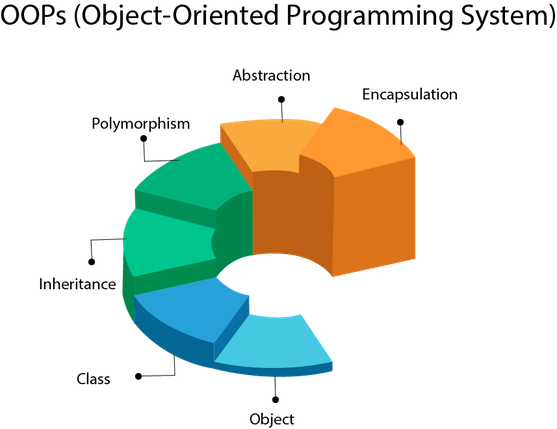
Java's object-oriented nature emphasizes modular and reusable code, facilitating the development of large-scale, maintainable applications. Key object-oriented principles such as encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism are fundamental to Java's design, enabling developers to build complex systems efficiently.